You must agree that:
If you’re showing your ads to the wrong people, no amount of budget, creativity, or clever copy will save you.
You’ll burn through cash fast and wonder why your click-through rates are low, your leads are junk, or your sales are stagnant.
That’s where target audiences come in.
Instead of spraying ads out to “everyone,” smart advertisers build precise audience segments based on:
- Intent
- Behavior
- Demographics
- Funnel stage
- And first-party data
Whether you’re running Google Ads or Meta Ads (Facebook & Instagram), your targeting determines:
- Who sees your ad
- How much you pay
- Whether your message even makes sense to that user
This guide breaks down how to find, build, and test target audiences that actually convert so your ads feel relevant, your results improve, and your costs drop.
Let’s stop advertising to everyone — and start reaching the people who actually matter.
What Is a Target Audience in Paid Advertising ?
A target audience is a specific group of people you want to reach with your ads based on who they are, what they do, and where they are in the buying journey.
It’s the opposite of “spray and pray.”
Instead of blasting your ad to everyone, you’re saying:
“I only want to show this ad to people who are likely to care, click, and convert.”
What Target Audiences Can Be Based On:
- Demographics – age, gender, location
- Interests – what they like, follow, or shop for
- Behaviors – website visits, video views, engagement
- Intent – what they’re searching for right now
- Lifecycle stage – first-time visitor vs. past customer
- Uploaded data – email lists, purchase history, CRM data
Why Targeting Matters So Much
Better targeting = lower costs and better results.
When your ads are shown to the right people:
- Your click-through rates (CTR) go up
- Your cost per click (CPC) goes down
- Your conversion rate improves
- Your return on ad spend (ROAS) grows
And perhaps most importantly:
Your audience sees your message and thinks,
“This is exactly what I need.”
Google vs. Meta Targeting — Key Differences
| Platform | Targeting Based On | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Google Ads | Search intent and audience signals | High-intent buyers, bottom-funnel |
| Meta Ads | Behavior & interest prediction | Discovery, awareness, retargeting |
Google shows your ads to people who are searching.
Meta shows your ads to people who are likely to care, even if they’re not searching yet.
Target Audience in Google Ads
Google is a powerful ad platform but it’s not just about keywords anymore.
Audience signals now play a critical role in:
- Who sees your search, display, and YouTube ads
- How your ads rank
- And how much you pay per click
Let’s explore how Google helps you target audiences to boost performance especially when combined with search intent.
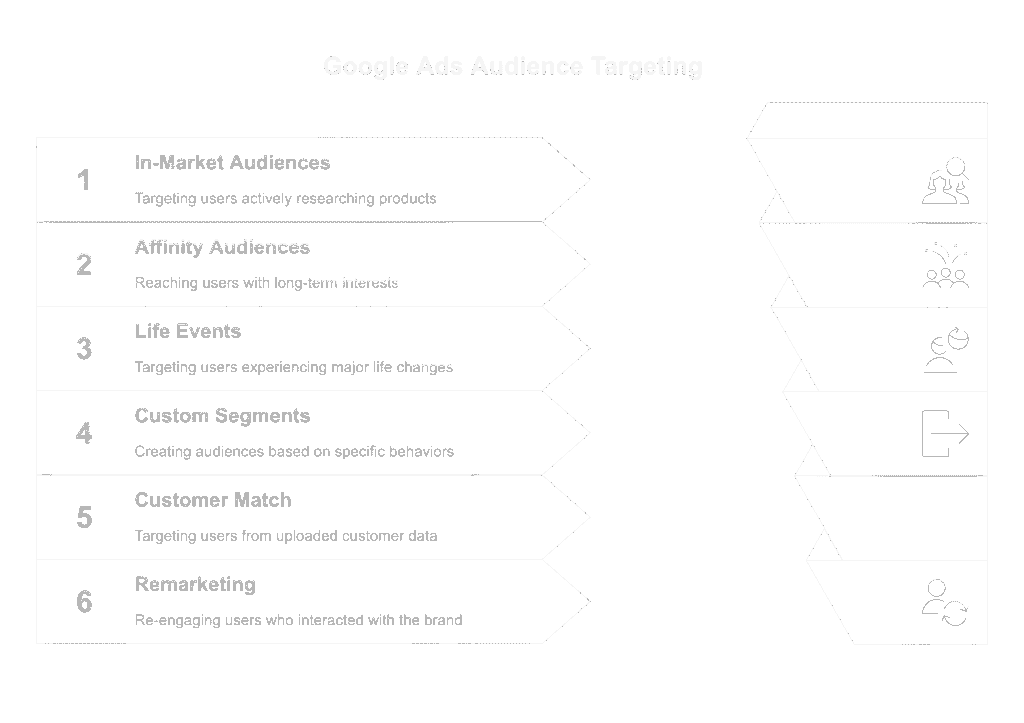
Key Audience Types in Google Ads
In-Market Audiences
Google knows what people are actively researching (based on their search + browsing behavior).
Use when:
- You want to reach people close to buying
- You’re running sales, product promos, or lead gen offers
Example: “Home renovation services” or “CRM software buyers”
Affinity Audiences
Long-term interest-based groups – think lifestyle, hobbies, and general preferences.
Use when:
- You’re building brand awareness
- You want to reach top-of-funnel users
Example: “Outdoor Enthusiasts” or “Tech News Junkies”
Life Events
Google can target users going through big changes like moving, graduating, or starting a new job.
Use when:
- Your offer ties into a major life moment
- You want to connect emotionally or time a campaign well
Example: “New Parents” or “College Graduation”
Custom Segments (formerly Custom Intent & Custom Affinity)
Create your own audience based on keywords, URLs, or apps they’ve engaged with.
Use when:
- You want to mimic competitor traffic
- You have a clear idea of buyer interests or behaviors
Example: Target people who searched for “Salesforce pricing” or visited HubSpot.com
Customer Match
Upload your email list or customer data and show ads to those users (or similar ones).
Use when:
- You want to retarget high-value leads
- You want to re-engage lapsed buyers
Bonus: You can build similar target audiences from these lists.
Remarketing (RLSA & Display)
Target people who visited your site, watched your videos, or interacted with your brand.
Use when:
- You want to stay top-of-mind
- You need to pull people back into the funnel
Remarketing works across Search, Display, YouTube, and Gmail.
Smart Audience Layering Tips
- Combine keywords + audiences for ultra-precise targeting (e.g., “CRM software” searchers who are also in-market for business tools)
- Use observation mode to track how different audience segments perform without restricting delivery
- Layer exclusions to avoid overlapping or irrelevant clicks
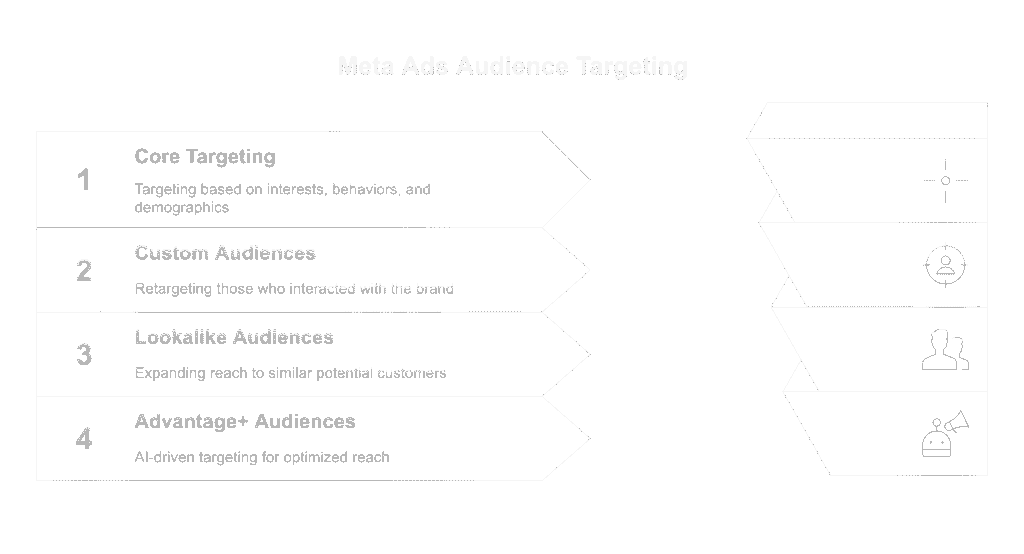
Target Audience in Meta Ads
Meta Ads (Facebook + Instagram) are built on one big strength:
They know what people care about even before those people realize it.
Unlike Google, which matches keywords to intent, Meta uses behavioral signals, interests, and engagement history to predict who’s most likely to respond to your ads.
Here’s how to use Meta’s targeting options strategically.
Core Targeting
Choose people based on:
- Interests (e.g. “Online shopping,” “Fitness,” “Marketing”)
- Behaviors (e.g. device usage, purchase activity)
- Demographics (age, gender, location, language)
Use when:
- You’re targeting cold audiences
- You want to test audience segments quickly
- You’re running awareness or top-of-funnel campaigns
Works well with compelling hooks and curiosity-driven creatives.
Custom Audiences
Create target audiences based on how people already interacted with your brand online or offline.
Sources include:
- Website visitors
- IG/Facebook engagers
- Video viewers
- Customer lists (email or phone)
- App users
- Offline events (in-store visits, POS data)
Use when:
- You want to retarget people who didn’t convert
- You’re nurturing warm leads
- You’re optimizing for mid or bottom-of-funnel
This is retargeting gold.
Lookalike Audiences
Meta takes your best audience (email list, customers, video viewers) and finds similar people who haven’t engaged with you yet.
You can choose:
- 1% (very similar, tighter targeting)
- 2–10% (broader, more reach)
Use when:
- You want to scale successful campaigns
- You have a strong Custom Audience
- You’re entering new markets
Always test 1% vs 2–3% lookalikes for best results.
Advantage+ Audiences (Broad Targeting with AI Control)
Meta’s machine learning chooses the targeting for you, based on your objective, creative, and conversion signals.
Use when:
- You’ve tested and optimized creatives
- You want to scale spend without over-controlling
- You’re in ecommerce or high-volume lead gen
Often outperforms manual targeting once you have momentum.
Smart Meta Targeting Tips:
- Stack custom audiences by behavior (e.g. viewed 75% of video + added to cart)
- Exclude converters to avoid wasted spend
- Test lookalikes alongside interest-based targeting
- Create funnel-specific audiences (cold, warm, hot)
- Refresh audiences monthly to avoid overlap/fatigue
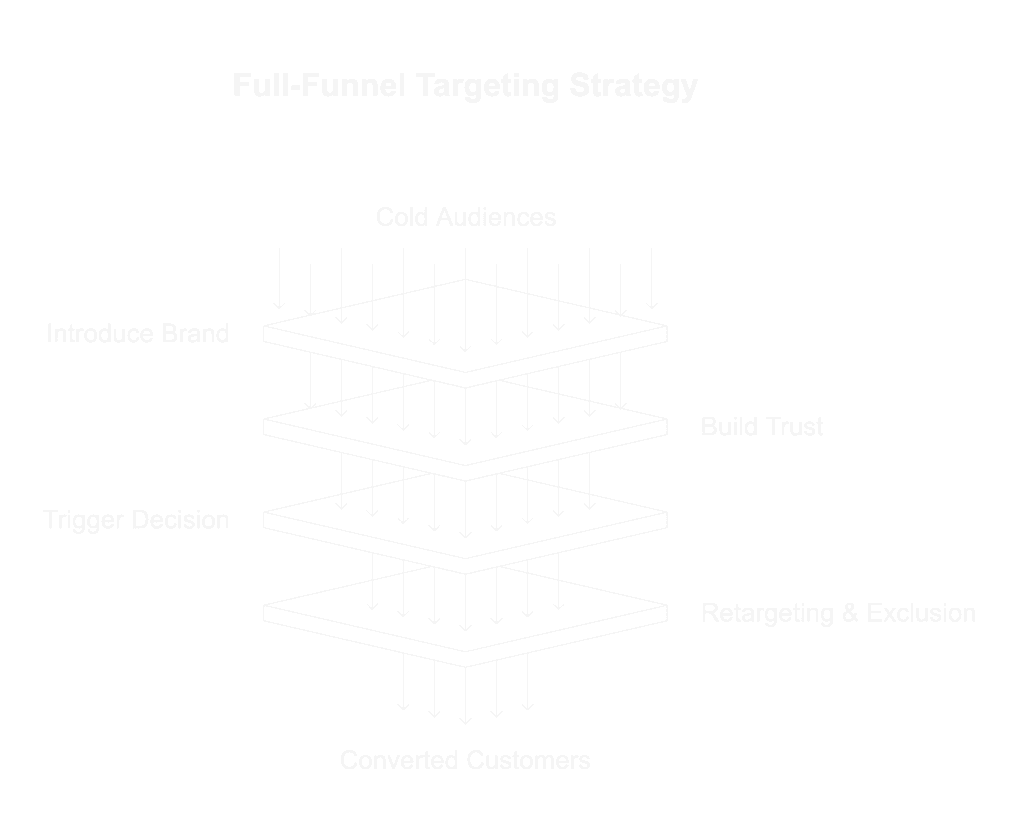
How to Build a Full-Funnel Target Audience Strategy
If you’re showing the same ad to everyone, you might be doing it wrong.
A proper full-funnel targeting strategy means reaching people at every stage of the buyer journey with the right message, offer, and format.
Here’s how to build a structure that guides cold traffic all the way to conversion (and beyond).
Top of Funnel (Cold Audiences)
People who don’t know your brand yet.
Audience Types:
- Meta: Interests, lookalikes, Advantage+
- Google: In-market, affinity, custom intent, YouTube cold viewers
Goals:
- Introduce brand or problem awareness
- Generate clicks, video views, page visits
- Seed retargeting audiences
Example:
Meta: 1% lookalike of buyers + “Online Business Owners”
Google: In-market for “CRM software”
Middle of Funnel (Warm Audiences)
They’ve seen your stuff — now they’re considering it.
Audience Types:
- Meta: Website visitors, engaged followers, video viewers (50–75%)
- Google: RLSA (Search retargeting), Display remarketing, custom segments
Goals:
- Build trust and authority
- Show proof, comparisons, case studies
- Move closer to conversion
Example:
Meta: Viewed product page but didn’t add to cart
Google: Visited 2+ pages but didn’t submit form
Bottom of Funnel (Hot Audiences)
They’re ready, they just need a push.
Audience Types:
- Meta: Cart abandoners, lead form openers, IG engagers
- Google: Remarketing lists, Customer Match
Goals:
- Trigger final decision
- Offer urgency or incentive
- Remove friction or doubt
Example:
Meta: “Your free trial is still waiting” ad
Google: Branded Search + past site visitor
Retargeting & Exclusion Logic
Don’t waste budget on people who already converted or see your ad too often.
- Use dynamic retargeting for ecommerce (product-level ads)
- Exclude past purchasers from cold traffic ads
- Exclude non-engagers from BOFU ads
- Cap frequency to avoid burnout
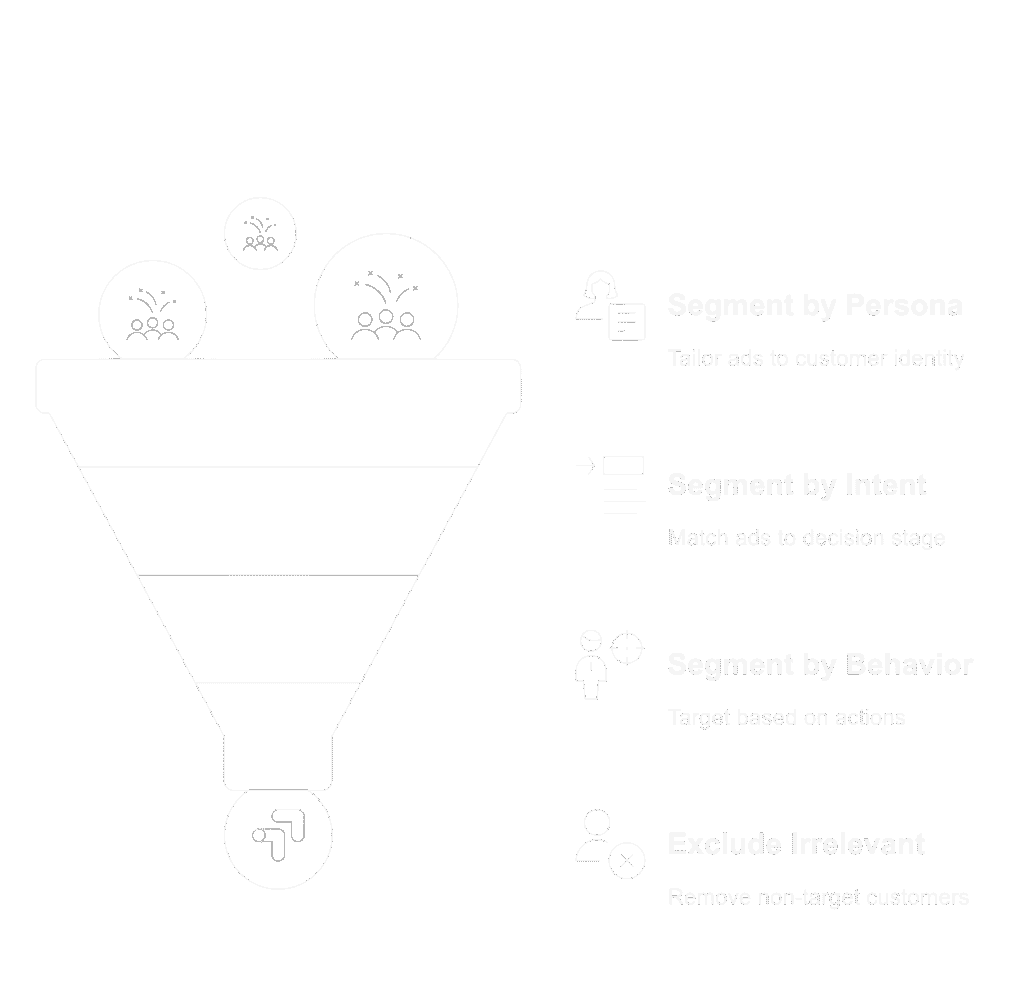
Target Audience Segments by Persona, Intent & Behavior
Not all customers are created equal.
A startup founder doesn’t think like a stay-at-home parent. A returning buyer doesn’t behave like someone discovering you for the first time.
That’s why smart advertisers don’t just target “audiences” they target personas, intent levels, and behaviors.
Let’s break that down.
Segment by Buyer Persona
Tailor your ads to match who your customers are.
Examples:
- First-time home buyers vs. real estate investors
- Agency owners vs. in-house marketers
- Budget-conscious vs. premium buyers
Use different:
- Copy angles
- Creative visuals
- Offers or pricing tiers
Tip: Mirror the customer’s language and pain points in your ad copy.
Segment by Intent Level
Where are they in their decision-making process?
| Intent Level | Audience Type | Best Use |
|---|---|---|
| Low Intent | Interest-based, broad lookalike | Awareness, education ads |
| Mid Intent | Engaged viewers, site visitors, lead magnets | Consideration-stage content |
| High Intent | Cart abandoners, branded search, form starters | Conversion-focused offers |
Match the CTA:
- Low = “Learn More”
- Mid = “See How It Works”
- High = “Book Now” or “Buy Today”
Segment by Behavior
Behavior = what people do, not just who they are.
Examples:
- Watched 75% of a product video
- Visited pricing page 3x in 7 days
- Opened an email but didn’t click
- Abandoned cart after adding 2+ items
Behavior-based target audiences are more accurate and scalable than guesswork-based personas.
Pro tip: On Meta, build Custom Audiences using behavioral triggers like:
- Time spent on site
- Video view thresholds
- Button clicks on landing pages
Don’t Forget Exclusions
Segmentation also means who NOT to target:
- Exclude buyers from intro offers
- Exclude new leads from “get started” CTAs
- Exclude cold users from product-level retargeting
- Exclude inactive users from high-frequency ad sets
Cleaner segmentation = better performance and less budget waste.
Testing & Optimizing Target Audiences
Your first target audience setup is just that — a starting point.
The real magic happens when you test, analyze, and refine your target audiences based on what actually works.
Let’s break down how to do it right.
A/B Testing Your Target Audiences
Just like creatives or copy, you should test audience segments head-to-head.
Test Variables:
- Interests vs lookalikes
- Broad targeting vs narrowed demographics
- Warm vs cold target audiences
- Custom audiences from different behaviors (video views vs. page visits)
Keep everything else constant (budget, creative, objective) so you can isolate performance differences.
Metrics That Matter Most
Watch for:
- CTR – Is the audience engaging?
- CPC – Is it cost-efficient to reach them?
- Conversion Rate – Are they taking action once they click?
- CPA/ROAS – Are they profitable?
Tip: A low CTR with a high ROAS can still be a win if look beyond surface metrics. (GA4)
When to Refresh or Retire Audiences
Signs of Audience Fatigue:
- Sudden drop in CTR or conversions
- Rising CPA with no creative change
- Frequency > 3.0 on Meta without scaling ROAS
- Google search terms becoming broader or less relevant
Refresh lookalikes, update exclusions, rotate creatives, or test a new offer.
Scaling Winning Audiences
Once you find a strong performer:
- Expand lookalike % (e.g. 1% → 2%)
- Test broader versions of that audience
- Move from ABO to CBO (Meta) or raise budgets in controlled steps
- Repurpose that audience across platforms (Meta → Google or vice versa)
Scale slowly to avoid volatility. Increase budgets 15–25% every few days.
Common Targeting Mistakes to Avoid
Even well-meaning campaigns can go sideways if your targeting isn’t dialed in.
Here are the mistakes we see most and how to fix them fast.
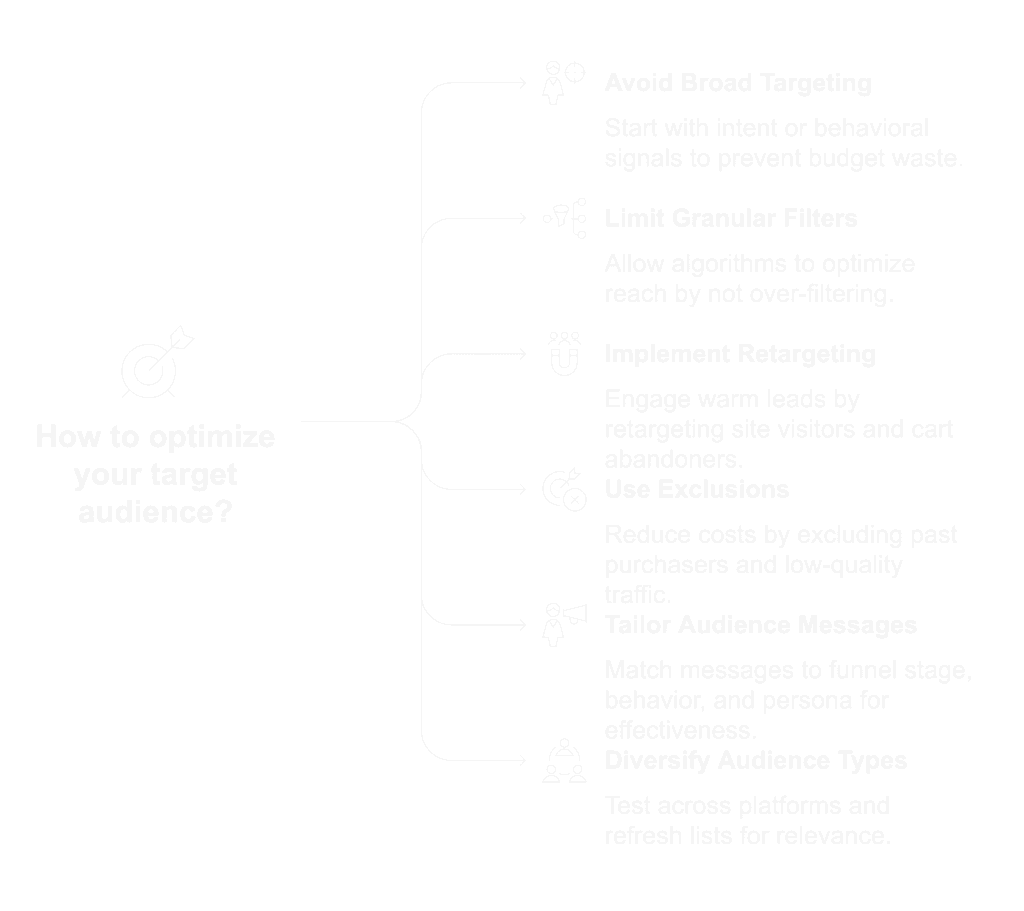
1. Targeting Too Broad (Too Soon)
Casting a wide net sounds smart but without data or structure, you’ll waste budget.
Start with intent or behavioral signals.
Go broad only after testing what converts.
2. Getting Too Granular (and Breaking Delivery)
On Meta especially, layering too many filters (age, interest, zip code, device) can choke reach.
Let the algorithm breathe especially when using Advantage+ or CBO.
3. Skipping Retargeting
Only running cold ads? You’re leaving money on the table.
Retarget site visitors, video watchers, form starters, and cart abandoners. These are your hottest leads.
4. Not Using Exclusions
Overlapping audiences = overexposure = higher costs.
Exclude:
- Past purchasers from lead ads
- Cold users from retargeting campaigns
- Low-quality traffic sources (as identified in GA or Meta)
5. Treating All Audiences the Same
Different audiences need different copy, creative, and offers.
Match your message to:
- Funnel stage
- Behavior
- Persona
6. Relying on One Audience Type
Interest-only. Or just lookalikes. Or one custom list from last year.
Diversify:
- Test across platforms
- Build lookalikes from behavior-based segments
- Refresh lists monthly for relevance
Final Word
Great ads don’t just persuade.
They reach the right people at the right time with the right message.
That’s what smart audience targeting delivers.
Whether you’re building lookalikes on Meta, layering intent signals in Google, or using first-party data to segment behavior…
Targeting is where scale, efficiency, and profit meet.
Don’t rely on guesswork.
Segment strategically. Test thoughtfully. And keep refining.
Because in paid advertising, who you target matters just as much as what you say.
Review our articles on ad strategy and ad copy optimization to be ready to launch your next campaign!
FAQs
How to find your target audience?
Analyze your existing customers, review competitor audiences, and use tools like Google Analytics or Meta Audience Insights to identify shared traits and behaviors.
How to create a target audience on a Google Workspace account?
You can’t create ad audiences directly in Google Workspace — you’ll need a connected Google Ads account to build and manage target audiences for campaigns.
Does your target audience have to be ranged by age?
No. Age is optional — target by behavior, interests, location, or purchase intent based on what matters most to your product or offer.
How to define a target audience?
Identify who your ideal customer is based on their needs, goals, and behaviors — then group them by shared traits like interests, location, or buying stage.